Generative Adversarial Networks with Transformers
While Vision Transformers have caught quite some attention in the community, it is still yet to be explored how such powerful models could work on building powerful GANs. Based on some recent progress in studying Transformers’ position encoding system, we want to explore the possibility of building a vision-oriented transformer block that is simple, light-weighted yet effective for a stable training of transformer GANs.
- Introduction
- Implementation
- From ALiBi to 2-D world: Euclidean Transformer
- Image Classification on CIFAR-10: Inspecting into the optimal choice of components for the discrminator
- Core Code Implementation
- GAN with Euclidean Transformer
- Extended References
- Code Repository & Video
Introduction
There’s already one successful attempt at training transformer GANs (TransGAN). However, as indicated by the paper, the proposed approach is showing the most significant shortcoming of almost all transformer-based models - it is more data-hungry compared to other architectures by a large margin. Inspired by the recent finding of an un-embedded, prior-based position encoding system (ALiBi), we hereby motivate our exploration of a simple, light-weighted yet effective design of a vision-oriented transformer block. We hope such design could alleviate the data efficiency problem of transformers whereas to maintain the merit of its ability to model long dependencies.
Implementation
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import BCEWithLogitsLoss, CrossEntropyLoss, MSELoss
from torch.nn import functional as F
from transformers.models.xlnet.modeling_xlnet import ACT2FN
from transformers.models.xlnet.modeling_xlnet import (
ModelOutput,
add_code_sample_docstrings,
add_start_docstrings,
add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward,
replace_return_docstrings,
)
from transformers.models.xlnet.modeling_xlnet import (
PoolerAnswerClass,
PoolerEndLogits,
PoolerStartLogits,
PreTrainedModel,
SequenceSummary,
apply_chunking_to_forward,
)
from transformers.models.xlnet.modeling_xlnet import logging
from transformers.models.xlnet.modeling_xlnet import XLNetConfig
class EuclideanTransformerRelativeAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(EuclideanTransformerRelativeAttention, self).__init__()
self.config = config
self.q = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(config.d_model, config.n_head, config.d_head))
self.k = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(config.d_model, config.n_head, config.d_head))
self.v = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(config.d_model, 4, config.n_head, config.d_head))
self.o = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(config.d_model, config.n_head, config.d_head))
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.d_model, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
@staticmethod
def generate_bias_map(h, w, nhead, device, eps=1e-10):
h_contribution = torch.arange(0, h, dtype=torch.float, device=device).reshape(h, 1).expand(h, w)
w_contribution = torch.arange(0, w, dtype=torch.float, device=device).reshape(1, w).expand(h, w)
vec_director = torch.stack([(h_contribution.reshape(h * w, 1) - (h_contribution.reshape(1, h * w))),
(w_contribution.reshape(h * w, 1) - (w_contribution.reshape(1, h * w)))]) # [2, h * w, h * w]
vec_director = (vec_director + eps) / (torch.norm(vec_director, p=1, dim=[-2, -1], keepdim=True) + eps)
vec_director = torch.cat((torch.abs(vec_director), -torch.abs(-vec_director)), dim=0)
h_contribution = h_contribution.reshape(h * w, 1) ** 2 + h_contribution.reshape(1, h * w) ** 2 - 2.0 * (h_contribution.reshape(h * w, 1) @ h_contribution.reshape(1, h * w))
w_contribution = w_contribution.reshape(h * w, 1) ** 2 + w_contribution.reshape(1, h * w) ** 2 - 2.0 * (w_contribution.reshape(h * w, 1) @ w_contribution.reshape(1, h * w))
all_dist = (h_contribution + w_contribution) ** 0.5
all_dist = all_dist * 8
m_contribution = -torch.arange(1, nhead + 1, dtype=torch.float, device=device).reshape(nhead, 1, 1) * 8 / nhead
m_contribution = torch.exp2(m_contribution)
bias_map = all_dist.reshape(1, h * w, h * w) * m_contribution
return bias_map, vec_director
def forward(self,
h,
h_pooling,
verbose=False
):
# h -> [batch_size, h, w, hidden_dim]
# attention_mask -> [batch_size, seq_len, seq_len]
# offset -> [batch, seq_len, seq_len]
# value head
# position-based key head
batch_size, h_size, w_size, hidden_dim = h.shape
_, pool_size, hidden_dim = h_pooling.shape
device = h.device
seq_len = h_size * w_size
h = h.reshape(batch_size, h_size * w_size, hidden_dim)
h = torch.cat((h, h_pooling), dim=1)
n_head = self.config.n_head
attention_mask = torch.ones(size=(1, 1, seq_len + pool_size, seq_len + pool_size), dtype=torch.float, device=device)
attention_mask[0, 0, seq_len:, :] = 0.0
attention_mask[0, 0, :, seq_len:] = 0.0
attention_mask[0, 0, seq_len:, seq_len:] = torch.diag(torch.ones((pool_size,), dtype=torch.float, device=device))
attention_mask[0, 0, seq_len:, 0:seq_len] = 1.0
# content-stream query head
q_head_h = torch.einsum("bih,hnd->bind", h, self.q)
k_head_h = torch.einsum("bih,hnd->bind", h, self.k)
v_head = torch.einsum("bih,hknd->biknd", h, self.v)
content_interaction = torch.einsum("bind,bjnd->bnij", q_head_h, k_head_h)
m_bias, vec_director = self.generate_bias_map(h_size, w_size, n_head, device=device)
m_bias_ = torch.zeros(n_head, seq_len + pool_size, seq_len + pool_size, dtype=torch.float, device=device)
vec_director_ = torch.ones(4, seq_len + pool_size, seq_len + pool_size, dtype=torch.float, device=device) / 4.0
m_bias_[:, 0:seq_len, 0:seq_len] = m_bias
vec_director_[:, 0:seq_len, 0:seq_len] = vec_director
alpha = content_interaction - m_bias_
# batch nhead seqlen seqlen
# for numerical stability
alpha = (alpha - (1.0 - attention_mask) * 1e30).log_softmax(dim=-1) - (1.0 - attention_mask) * 1e30
# exp_alpha_masked = exp_alpha * attention_mask
normalized_alpha = alpha.softmax(dim=-1) #exp_alpha_masked / (exp_alpha_masked.sum(dim=-1, keepdims=True))
normalized_alpha_select_angle = torch.einsum("kij,bnij->bknij", vec_director_, normalized_alpha)
reduced_v_head = torch.einsum("bknij,bjknd->bind", normalized_alpha_select_angle, v_head)
transformed_reduced_v_head = torch.einsum("bind,hnd->bih", reduced_v_head, self.o)
transformed_reduced_v_head = self.dropout(transformed_reduced_v_head)
h_comp = self.layer_norm(transformed_reduced_v_head)
return h_comp
class EuclideanTransformerFeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(EuclideanTransformerFeedForward, self).__init__()
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.d_model, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
self.layer_1 = nn.Linear(config.d_model, config.d_inner)
self.layer_2 = nn.Linear(config.d_inner, config.d_model)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
if isinstance(config.ff_activation, str):
self.activation_function = ACT2FN[config.ff_activation]
else:
self.activation_function = config.ff_activation
def forward(self, inp):
output = inp
output = self.layer_1(output)
output = self.activation_function(output)
output = self.dropout(output)
output = self.layer_2(output)
output = self.dropout(output)
output = self.layer_norm(output + inp)
return output
class EuclideanTransformerLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.rel_attn = EuclideanTransformerRelativeAttention(config)
self.ff = EuclideanTransformerFeedForward(config)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
self.chunk_size_feed_forward = config.chunk_size_feed_forward
self.seq_len_dim = 1
def forward(
self,
pixel_embeddings,
semantic_embeddings,
verbose=False
):
batch_size, h_size, w_size, hidden_dim = pixel_embeddings.shape
seq_len = h_size * w_size
h_comp = self.rel_attn(
h=pixel_embeddings,
h_pooling=semantic_embeddings,
verbose=verbose
)
h_comp = self.ff(h_comp)
h_, h_pooling_ = h_comp[:, 0:seq_len, :], h_comp[:, seq_len:, :]
pixel_embeddings, semantic_embeddings = h_.reshape(batch_size, h_size, w_size, hidden_dim), h_pooling_
return pixel_embeddings, semantic_embeddings
class EuclideanTransformerPreTrainedModel(PreTrainedModel):
"""
An abstract class to handle weights initialization and a simple interface for downloading and loading pretrained
models.
"""
config_class = XLNetConfig
base_model_prefix = "transformer"
def _init_weights(self, module):
"""Initialize the weights."""
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear) or isinstance(module, nn.Conv2d):
# Slightly different from the TF version which uses truncated_normal for initialization
# cf https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/5617
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
if module.bias is not None:
module.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.Embedding):
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
if module.padding_idx is not None:
module.weight.data[module.padding_idx].zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.LayerNorm):
module.bias.data.zero_()
module.weight.data.fill_(1.0)
elif isinstance(module, EuclideanTransformerRelativeAttention):
for param in [
module.q,
module.k,
module.v,
module.o,
]:
param.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
elif isinstance(module, EuclideanTransformerModel):
module.pool_emb.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
module.pos_emb.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
class EuclideanTransformerActivation(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: XLNetConfig):
super().__init__()
if isinstance(config.ff_activation, str):
self.activation_function = ACT2FN[config.ff_activation]
else:
self.activation_function = config.ff_activation
def forward(self, x):
return self.activation_function(x)
class EuclideanTransformerModel(EuclideanTransformerPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config: XLNetConfig, addon_absolute_pos=False):
super().__init__(config)
self.mem_len = config.mem_len
self.reuse_len = config.reuse_len
self.d_model = config.d_model
self.same_length = config.same_length
self.attn_type = config.attn_type
self.bi_data = config.bi_data
self.clamp_len = config.clamp_len
self.n_layer = config.n_layer
width = 8
self.width = width
self.input_proj = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3,
out_channels=config.d_model,
kernel_size=8,
stride=8,
padding=0,
)
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.d_model, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
self.pool_emb = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(1, 1, config.d_model))
self.pos_emb = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(64 // width, 64 // width, config.d_model))
self.layer = nn.ModuleList([EuclideanTransformerLayer(config) for _ in range(config.n_layer)])
# self._layer = nn.ModuleList([EuclideanTransformerLayer(config)])
# self.layer = [self._layer[0]] * config.n_layer
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
self.init_weights()
def forward(self,
input_pixels
):
input_pixels = self.input_proj(input_pixels)
pixel_embeddings = input_pixels.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
batch_size, h_size, w_size, channel_size = pixel_embeddings.shape
semantic_embeddings = self.pool_emb.expand(batch_size, 1, self.config.d_model)
down_sampling = [0, 3, 8,]
for i, layer_module in enumerate(self.layer):
batch_size, h_size, w_size, channel_size = pixel_embeddings.shape
pixel_embeddings, semantic_embeddings = layer_module(
pixel_embeddings=pixel_embeddings,
semantic_embeddings=semantic_embeddings,
)
# if i in down_sampling:
# pixel_embeddings = pixel_embeddings.reshape(batch_size, h_size//2, 2, w_size//2, 2, channel_size)
# pixel_embeddings = pixel_embeddings[:, :, -1, :, -1, :]
return pixel_embeddings, semantic_embeddings
We start with a detailed discussion of ALiBi, assuming our audience have a basic understanding of the following components:
- Transformers, Multi-headed attention and its in-layer transformations from Attention is all you need
- Sinusoidal Position Embedding
- Additive (Original implementation from Attention is all you need)
- Multiplicative aka. Rotary Position Embedding is introduced by Roformer and popularized by an unofficial GPT-3 replica GPT-J
- Relative Position Encoding
- T-5 Bias-based, distance-wise
- Transformer-XL/XLNet Bias-based, directed distance-wise
ALiBi proposes a light-weight implementation of relative position encoding for decoder transformers. It does not only save the total number of parameters, but also proven beneficial for such models to scale up to extrapolated samples. We would not be exploring much on the latter but focusing more on the former.
ALiBi proposes the bias-based position encoding as such:
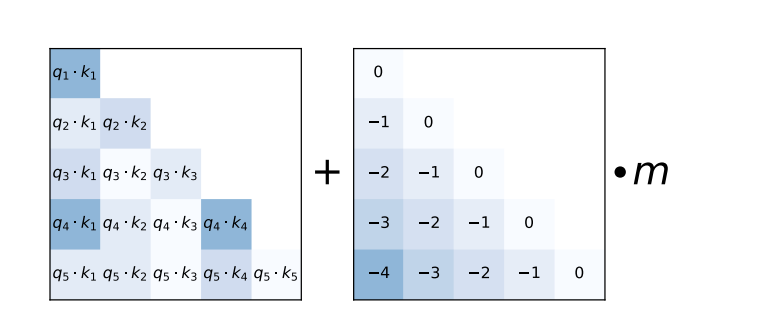
where m is the smoothing parameter that allows attention heads to interpolate between taking the bias into account and completely ignoring it in the exponential scale.
However, ALiBi was originally designed for decoder transformers that uses a upper-triangular, masked attention where each token is only attending to previous tokens. The direction of the attentions are implicitly determined at the very beginning. To deploy this component for bi-directional, 2-D transformer models, we need to modify it so that it takes the basic components of 2-D euclidean geometry into account, resulting in our proposed method, Euclidean Transformer.
From ALiBi to 2-D world: Euclidean Transformer
It is a natural idea to directly extend the idea in ALiBi to form the distance matrix for Euclidean geometry. We hereby discuss how we are addressing the direction issues. Note that in a 2-D world, for an arbitrary vector, if we use non-negative parameters to represent it, a direct choice is to use four of those so that the forward and backward directions of each dimension is separately represented. This figure shows the general idea:
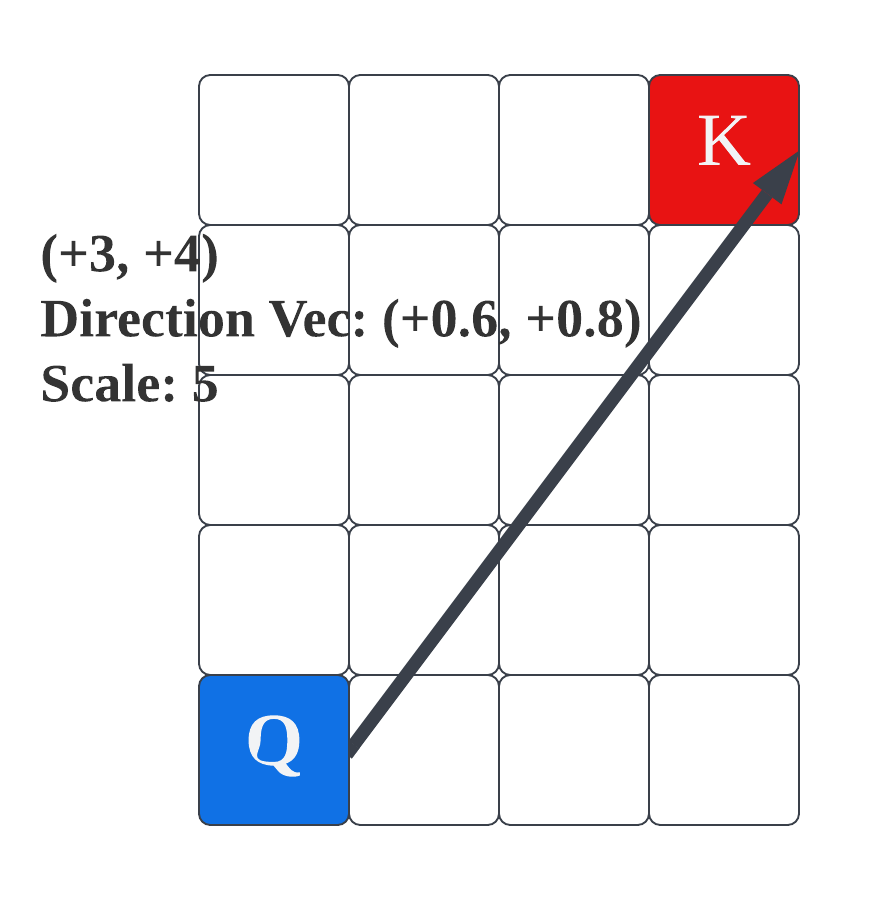
We then modify the alpha from a sequence of scalars w.r.t. each token to a sequence of such direction vectors. Since we’ve taken into account the distance in the bias term, we use normalized direction vectors. The value-transformation in each Euclidean Transformer layers is respectively adjusted to correctly interact with such changes. For ease of notation, we denote the scale of alpha to be $\mathbf{A}^i$ and its direction to be $\mathbf{D}^i$.
Given the input embeddings $\mathbf{E}^{i-1}$, each Euclidean Transformer layer can be formulated as follows. $\mathbf{W}^i_*$ are model parameters. $\mathbf{R}$ is the distance matrix. \(\mathbf{Q}^i,\mathbf{K}^i=\mathbf{W}_q^i\mathbf{E}^{i-1},\mathbf{W}_{k,E}^i\mathbf{E}^{i-1}\\ \mathbf{V}^i=\mathbf{W}_v^i\mathbf{E}^{i-1}\\ \mathbf{A}^i=\mathbf{Q}^{i\top}\mathbf{K}^i - m^\top \mathbf{R} \\ \mathbf{V}_{\text{reduced}}^{i}=\text{Masked-Softmax}(\mathbf{A}^i)(\mathbf{D}^i\mathbf{V}^i)\\ \mathbf{V}_{\text{skipconn}}^{i}=\mathbf{V}_{\text{reduced}}^{i}+\mathbf{E}^{i-1} \\ \mathbf{E}^i=\text{Feed-Forward}_{\theta^{i}}(\mathbf{V}_{\text{skipconn}}^{i})\)
Image Classification on CIFAR-10: Inspecting into the optimal choice of components for the discrminator
According to previous study as in TransGAN, the bottleneck of applying transformers to image generation with GAN algorithm mostly comes from transformer-based discriminators’ lack of inductive bias. Before we step into the GAN training problem, we want to investigate whether our proposed Euclidean Transformer is indeed a better alternative to ViT when super large-scale pretraining is no longer available.
In addition to results from just using the basic components of Euclidean transformer, we also conduct an ablative study of different common choices of extra components in vision transformers, including after-layer downsampling via strided conv/pooling etc.
We compare against previous data-hungry transformers, a strong convolution baseline and MLP baseline. The results are shown as follows:
| CIFAR-10 Test Acc. | GPU Mem | |
|---|---|---|
| ViT (no pretrain) | 56.81% | 14.1G |
| ResNet-18 | 91.25% | - |
| MLP | 36.71% | - |
| MLP Mixer (no pretrain) | 60.33% | 1.2G |
| EucT (4x4 patch) | 73.46% | 4.6G |
| +strided conv downsample | 73.89% | 2.3G |
| +AvgPooling 2x2 | 72.21% | 2.1G |
| w/o residual connection | 50.89% | 4.3G |
| w/o distance bias | 69.85% | 4.3G |
| w/o directed alpha | 63.72% | 4.3G |
| w/o distance bias/directed alpha | 55.13% | 4.3G |
As is inspected by the experiments, the proposed EucT significantly improved the data efficiency and achieved reasonable memory efficiency. We didn’t use any data augmentation for all models. Some of the reported performance are adopted from Vision XFormers.
Introducing downsamling helps further improving computation efficiency but the overall model performance is similar.
To study the effect of our proposed position encoding mechanism, we conduct an ablation study on the two factors, directed alpha and 2-D ALiBi distance bias. When only the distance bias term is removed, the model performance degeneration is, surprisingly, not very severe. The convergence of the model is, though, slowed by at least 2 times in terms of #epochs required. We suspect this is because that given the directed alpha/value transformation, the model can gradually learn the distance information by counting how many times each direction vector appears. This is confirmed by the ablation study of further removing the directed alpha mechanism. The performance degeneration is then servere enough to the level of MLP Mixer (no pretrain).
Core Code Implementation
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import BCEWithLogitsLoss, CrossEntropyLoss, MSELoss
from torch.nn import functional as F
from transformers.models.xlnet.modeling_xlnet import ACT2FN
from transformers.models.xlnet.modeling_xlnet import (
ModelOutput,
add_code_sample_docstrings,
add_start_docstrings,
add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward,
replace_return_docstrings,
)
from transformers.models.xlnet.modeling_xlnet import (
PoolerAnswerClass,
PoolerEndLogits,
PoolerStartLogits,
PreTrainedModel,
SequenceSummary,
apply_chunking_to_forward,
)
from transformers.models.xlnet.modeling_xlnet import logging
from transformers.models.xlnet.modeling_xlnet import XLNetConfig
class EuclideanTransformerRelativeAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(EuclideanTransformerRelativeAttention, self).__init__()
self.config = config
self.q = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(config.d_model, config.n_head, config.d_head))
self.k = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(config.d_model, config.n_head, config.d_head))
self.v = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(config.d_model, 4, config.n_head, config.d_head))
self.o = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(config.d_model, config.n_head, config.d_head))
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.d_model, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
@staticmethod
def generate_bias_map(h, w, nhead, device, eps=1e-10):
h_contribution = torch.arange(0, h, dtype=torch.float, device=device).reshape(h, 1).expand(h, w)
w_contribution = torch.arange(0, w, dtype=torch.float, device=device).reshape(1, w).expand(h, w)
vec_director = torch.stack([(h_contribution.reshape(h * w, 1) - (h_contribution.reshape(1, h * w))),
(w_contribution.reshape(h * w, 1) - (w_contribution.reshape(1, h * w)))]) # [2, h * w, h * w]
vec_director = (vec_director + eps) / (torch.norm(vec_director, p=2, dim=[-2, -1], keepdim=True) + eps)
vec_director = torch.cat((torch.relu(vec_director), torch.relu(-vec_director)), dim=0)
h_contribution = h_contribution.reshape(h * w, 1) ** 2 + h_contribution.reshape(1, h * w) ** 2 - 2.0 * (h_contribution.reshape(h * w, 1) @ h_contribution.reshape(1, h * w))
w_contribution = w_contribution.reshape(h * w, 1) ** 2 + w_contribution.reshape(1, h * w) ** 2 - 2.0 * (w_contribution.reshape(h * w, 1) @ w_contribution.reshape(1, h * w))
all_dist = (h_contribution + w_contribution) ** 0.5
m_contribution = -torch.arange(1, nhead + 1, dtype=torch.float, device=device).reshape(nhead, 1, 1) * 8 / nhead
m_contribution = torch.exp2(m_contribution)
bias_map = all_dist.reshape(1, h * w, h * w) * m_contribution
return bias_map, vec_director
def forward(self,
h,
h_pooling,
verbose=False
):
# h -> [batch_size, h, w, hidden_dim]
# attention_mask -> [batch_size, seq_len, seq_len]
# offset -> [batch, seq_len, seq_len]
# value head
# position-based key head
batch_size, h_size, w_size, hidden_dim = h.shape
_, pool_size, hidden_dim = h_pooling.shape
device = h.device
seq_len = h_size * w_size
h = h.reshape(batch_size, h_size * w_size, hidden_dim)
h = torch.cat((h, h_pooling), dim=1)
n_head = self.config.n_head
attention_mask = torch.ones(size=(1, 1, seq_len + pool_size, seq_len + pool_size), dtype=torch.float, device=device)
attention_mask[0, 0, seq_len:, :] = 0.0
attention_mask[0, 0, :, seq_len:] = 0.0
attention_mask[0, 0, seq_len:, seq_len:] = torch.diag(torch.ones((pool_size,), dtype=torch.float, device=device))
attention_mask[0, 0, seq_len:, 0:seq_len] = 1.0
# content-stream query head
q_head_h = torch.einsum("bih,hnd->bind", h, self.q)
k_head_h = torch.einsum("bih,hnd->bind", h, self.k)
v_head = torch.einsum("bih,hknd->biknd", h, self.v)
content_interaction = torch.einsum("bind,bjnd->bnij", q_head_h, k_head_h)
m_bias, vec_director = self.generate_bias_map(h_size, w_size, n_head, device=device)
m_bias_ = torch.zeros(n_head, seq_len + pool_size, seq_len + pool_size, dtype=torch.float, device=device)
vec_director_ = torch.ones(4, seq_len + pool_size, seq_len + pool_size, dtype=torch.float, device=device) / 4.0
m_bias_[:, 0:seq_len, 0:seq_len] = m_bias
vec_director_[:, 0:seq_len, 0:seq_len] = vec_director
alpha = content_interaction - m_bias_
# batch nhead seqlen seqlen
# for numerical stability
alpha = (alpha - (1.0 - attention_mask) * 1e30).log_softmax(dim=-1) - (1.0 - attention_mask) * 1e30
# exp_alpha_masked = exp_alpha * attention_mask
normalized_alpha = alpha.softmax(dim=-1) #exp_alpha_masked / (exp_alpha_masked.sum(dim=-1, keepdims=True))
normalized_alpha_select_angle = torch.einsum("kij,bnij->bknij", vec_director_, normalized_alpha)
reduced_v_head = torch.einsum("bknij,bjknd->bind", normalized_alpha_select_angle, v_head)
transformed_reduced_v_head = torch.einsum("bind,hnd->bih", reduced_v_head, self.o)
transformed_reduced_v_head = self.dropout(transformed_reduced_v_head)
h_comp = self.layer_norm(transformed_reduced_v_head + h)
return h_comp
class EuclideanTransformerFeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(EuclideanTransformerFeedForward, self).__init__()
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.d_model, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
self.layer_1 = nn.Linear(config.d_model, config.d_inner)
self.layer_2 = nn.Linear(config.d_inner, config.d_model)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
if isinstance(config.ff_activation, str):
self.activation_function = ACT2FN[config.ff_activation]
else:
self.activation_function = config.ff_activation
def forward(self, inp):
output = inp
output = self.layer_1(output)
output = self.activation_function(output)
output = self.dropout(output)
output = self.layer_2(output)
output = self.dropout(output)
output = self.layer_norm(output + inp)
return output
class EuclideanTransformerLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.rel_attn = EuclideanTransformerRelativeAttention(config)
self.ff = EuclideanTransformerFeedForward(config)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
self.down_sampling_proj = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=config.d_model,
out_channels=config.d_model,
kernel_size=2,
stride=2,
padding=0,
)
self.chunk_size_feed_forward = config.chunk_size_feed_forward
self.seq_len_dim = 1
def forward(
self,
pixel_embeddings,
semantic_embeddings,
down_sampling=True,
verbose=False
):
batch_size, h_size, w_size, hidden_dim = pixel_embeddings.shape
seq_len = h_size * w_size
h_comp = self.rel_attn(
h=pixel_embeddings,
h_pooling=semantic_embeddings,
verbose=verbose
)
h_comp = self.ff(h_comp)
h_, h_pooling_ = h_comp[:, 0:seq_len, :], h_comp[:, seq_len:, :]
pixel_embeddings, semantic_embeddings = h_.reshape(batch_size, h_size, w_size, hidden_dim), h_pooling_
if down_sampling:
pixel_embeddings = self.down_sampling_proj(pixel_embeddings.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)).permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
# if h_size % 2 == 0 and w_size % 2 == 0:
# pixel_embeddings = pixel_embeddings.reshape(batch_size, h_size // 2, 2, w_size // 2, 2, hidden_dim).mean(dim=2).mean(dim=-2)
# else:
# pixel_embeddings = pixel_embeddings[:, 1:, 1:, :].reshape(batch_size, h_size // 2, 2, w_size // 2, 2, hidden_dim).mean(dim=2).mean(dim=-2)
return pixel_embeddings, semantic_embeddings
class EuclideanTransformerPreTrainedModel(PreTrainedModel):
"""
An abstract class to handle weights initialization and a simple interface for downloading and loading pretrained
models.
"""
config_class = XLNetConfig
base_model_prefix = "transformer"
def _init_weights(self, module):
"""Initialize the weights."""
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear) or isinstance(module, nn.Conv2d):
# Slightly different from the TF version which uses truncated_normal for initialization
# cf https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/5617
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
if module.bias is not None:
module.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.Embedding):
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
if module.padding_idx is not None:
module.weight.data[module.padding_idx].zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.LayerNorm):
module.bias.data.zero_()
module.weight.data.fill_(1.0)
elif isinstance(module, EuclideanTransformerRelativeAttention):
for param in [
module.q,
module.k,
module.v,
module.o,
]:
param.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
elif isinstance(module, EuclideanTransformerModel):
module.pool_emb.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
# module.pos_emb.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
class EuclideanTransformerActivation(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: XLNetConfig):
super().__init__()
if isinstance(config.ff_activation, str):
self.activation_function = ACT2FN[config.ff_activation]
else:
self.activation_function = config.ff_activation
def forward(self, x):
return self.activation_function(x)
class EuclideanTransformerModel(EuclideanTransformerPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config: XLNetConfig, addon_absolute_pos=False):
super().__init__(config)
self.mem_len = config.mem_len
self.reuse_len = config.reuse_len
self.d_model = config.d_model
self.same_length = config.same_length
self.attn_type = config.attn_type
self.bi_data = config.bi_data
self.clamp_len = config.clamp_len
self.n_layer = config.n_layer
self.input_proj = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3,
out_channels=config.d_model,
kernel_size=4,
stride=4,
padding=0,
)
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.d_model, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
self.pool_emb = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(1, 1, config.d_model))
self.layer = nn.ModuleList([EuclideanTransformerLayer(config) for _ in range(config.n_layer)])
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout)
self.init_weights()
def forward(self,
input_pixels
):
input_pixels = self.input_proj(input_pixels)
pixel_embeddings = input_pixels.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
batch_size, h_size, w_size, channel_size = pixel_embeddings.shape
semantic_embeddings = self.pool_emb.expand(batch_size, 1, self.config.d_model)
down_sampling = []
for i, layer_module in enumerate(self.layer):
batch_size, h_size, w_size, channel_size = pixel_embeddings.shape
pixel_embeddings, semantic_embeddings = layer_module(
pixel_embeddings=pixel_embeddings,
semantic_embeddings=semantic_embeddings,
down_sampling=(i in down_sampling)
)
return pixel_embeddings, semantic_embeddings
GAN with Euclidean Transformer
We then use the proposed model to construct a out-of-box usable GAN framework. We choose WGAN-LP (improved GP) as our training algorithm. Since we’ll be dealing with comparatively smaller images, we still use 4x4 patches as the represenation. We don’t use downsampling in discriminator. For generator upsampling, we use transposed convolution.
We tested our results on MNIST digit generation problem. Unfortunately, we had problems applying the method to build up an efficient enough generator. We suspect this it seems the proposed method is not quite compatible with the WGAN object, as computing the earth mover’s distance may require more accurate control of the geometry than what the current design can support. We hereby list some of the typical failed cases:




As we can see from these examples, although it did get the high-level pattern of the digits, the model does not seem to quite generate/capture useful signals from the adversarial training process. Whether this is a result bottlenecked by the discriminator or the generator still needs further investigation.
Extended References
[1] Jiang Y, Chang S, Wang Z. Transgan: Two transformers can make one strong gan[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.07074, 2021, 1(2): 7.
[2] Press O, Smith N A, Lewis M. Train short, test long: Attention with linear biases enables input length extrapolation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.12409, 2021.
[3] Durall R, Frolov S, Hees J, et al. Combining transformer generators with convolutional discriminators[C]//German Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Künstliche Intelligenz). Springer, Cham, 2021: 67-79.
[4] Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks[C]//International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2017: 214-223.
[5] Gulrajani I, Ahmed F, Arjovsky M, et al. Improved training of wasserstein gans[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.00028, 2017.
Code Repository & Video
[1] WGAN/WGAN-GP
[2] TransGAN
[3] WGAN-T (Ours)
[4] Recorded Video